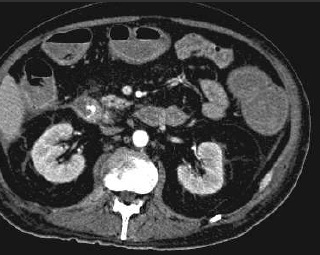
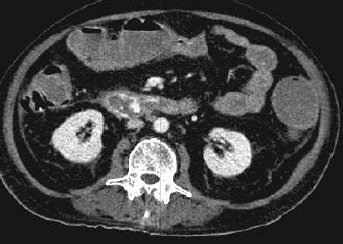
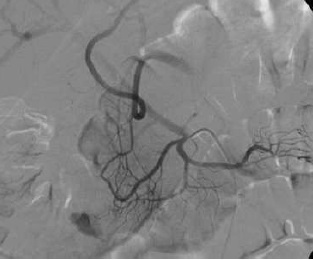
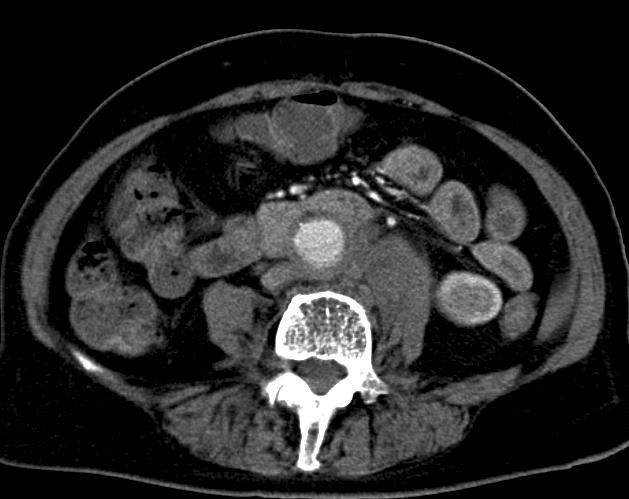
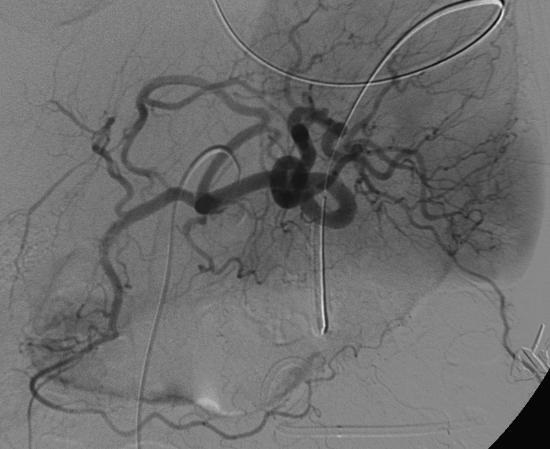
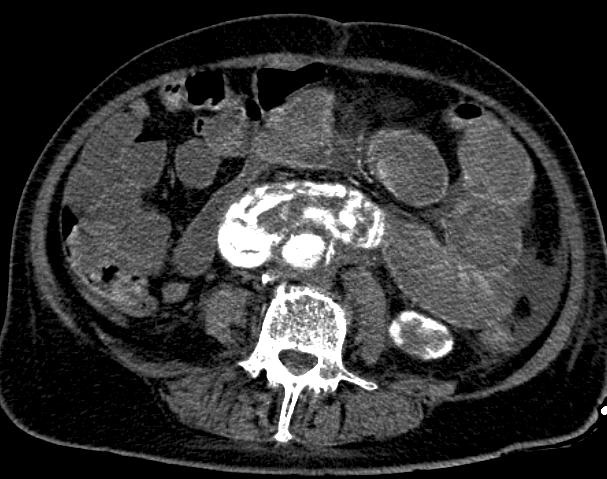
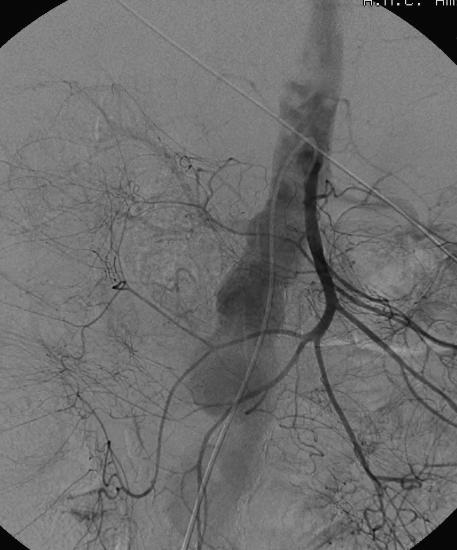
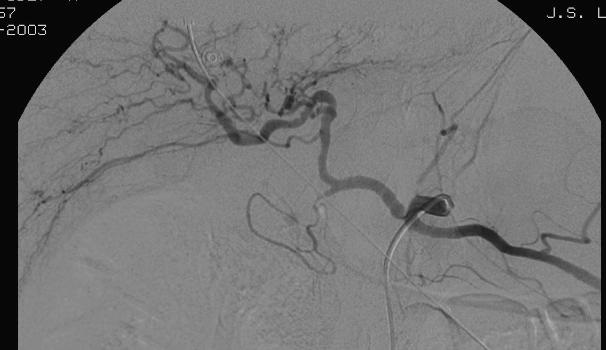
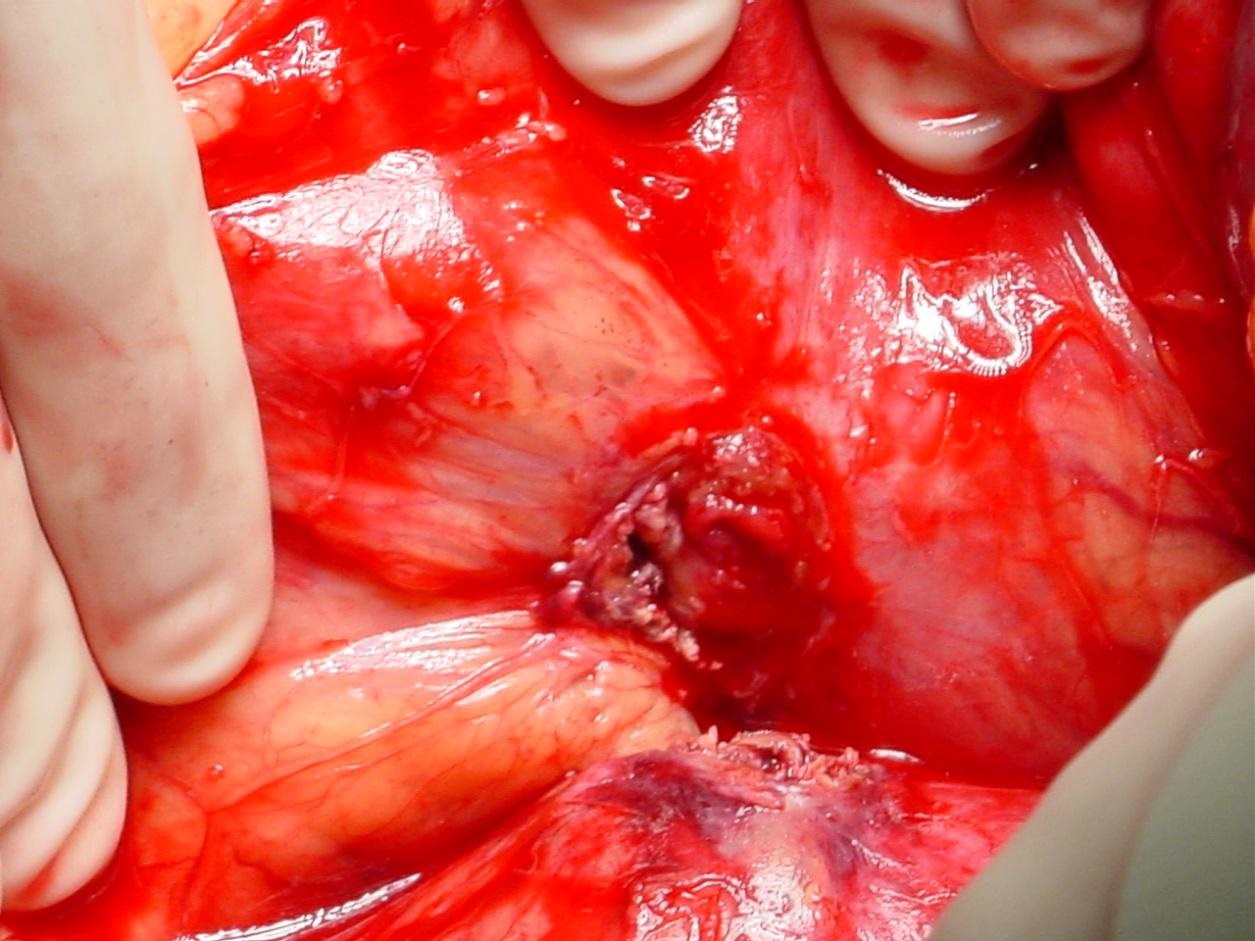
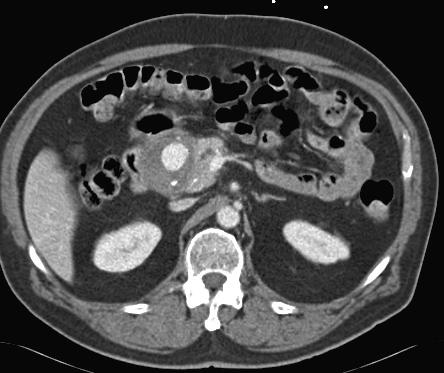
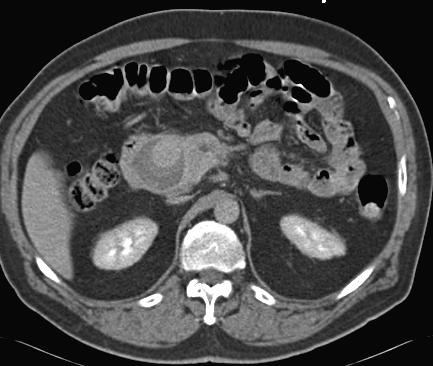
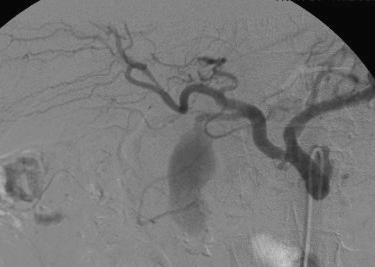
至少20年前我们诊断消化道出血依赖血管造影(angiography),内窥镜(endoscopy)和核素扫描(scintigraphy)。但如果没有这些依赖专门人员操作的检查时,怎么办? CTA血管造影诊断消化道出血究竟是一种向往或渴望,还是消化道诊断策略中的要求,甚至强制。 有关血管造影的历史(angiography history)
CTA 对于消化道出血的诊断又分为 CTA可以用于任何形式的消化道出血
相关文献
Yoon et al. Acute massive GI bleeding: detection and localization with arterial phase MDCT. Radiology, 2006: 239, 160-7
Scheffel et al. Acute GI bleeding: detection of source and etiology with MDCT. Eur Radiol. 2007: 17,1555-65
Ko et al. Localialization of bleeding using MDCT in patietns with signs of acute GI hemorrhage. Rofo 2005: 177, 1649-54
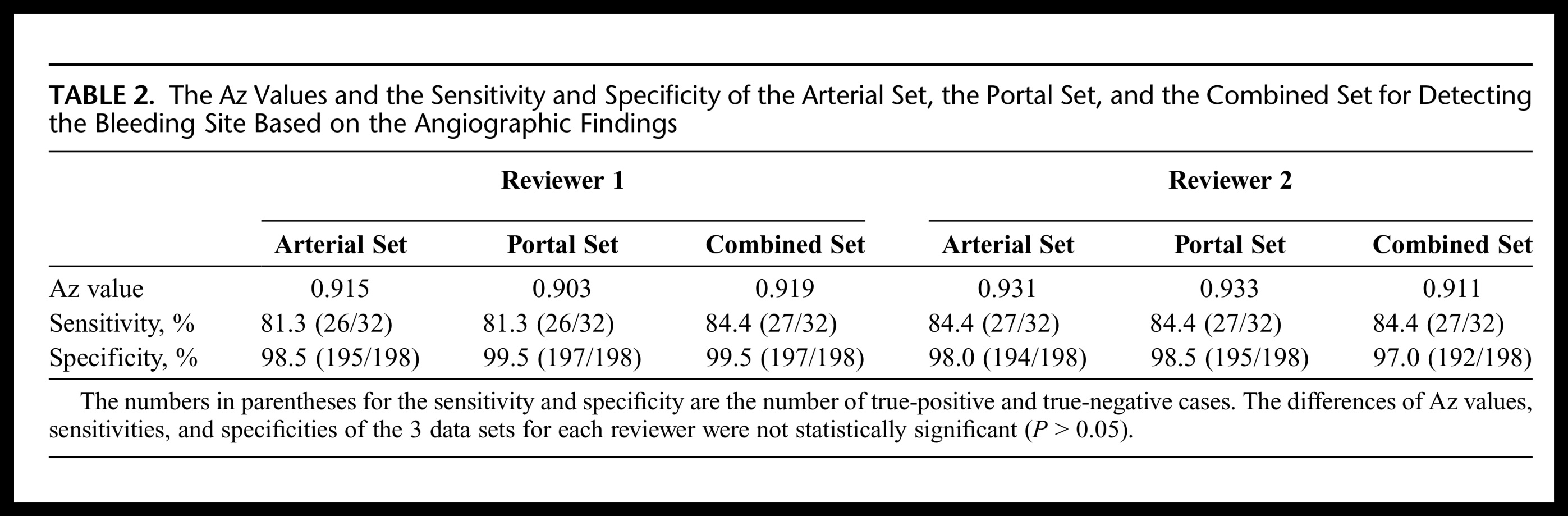
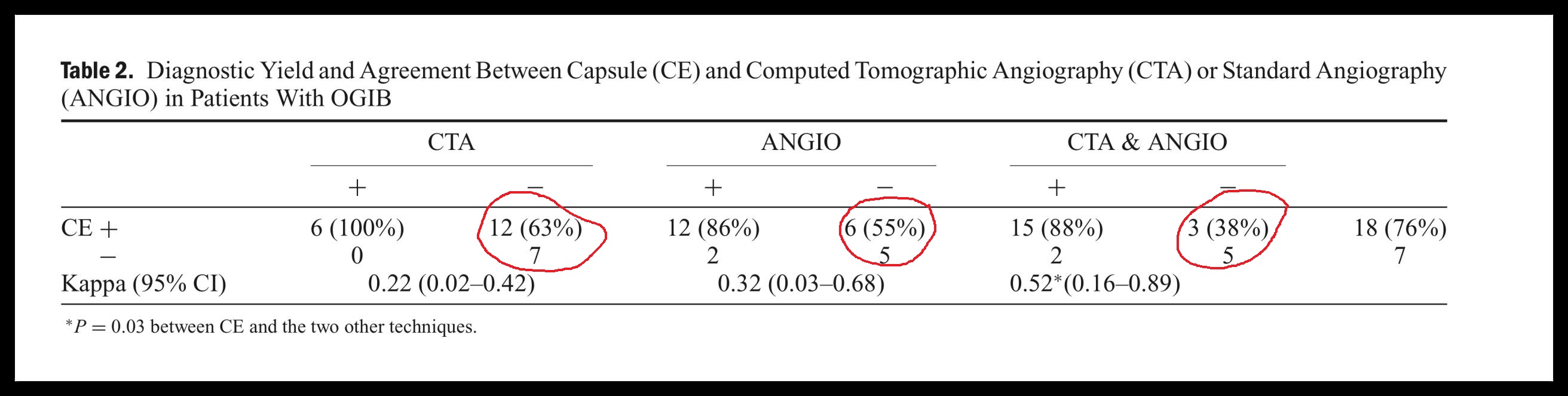
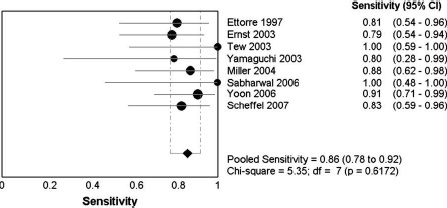
CT血管造影在诊断急性消化道出血有用性(阴性的有用性,阳性的有用性)如下表 CTA诊断急性消化道出血meta分析(2008)有关文献记载急性消化道CTA的结果(P. Goffette, CIRSE 2009)
from Jaeckle T, Eur Radiol, 2008, 18:1406 另外一篇文章可看 Diagnostic accuracy of CT angiography in acute gastrointestinal bleedingby Angela Chua and Ridley (Sidney) in J Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 2008 CTA诊断急性消化道出血meta分析(2011)from Wu et al. World Journal of Gastroenterology 2011 copycat 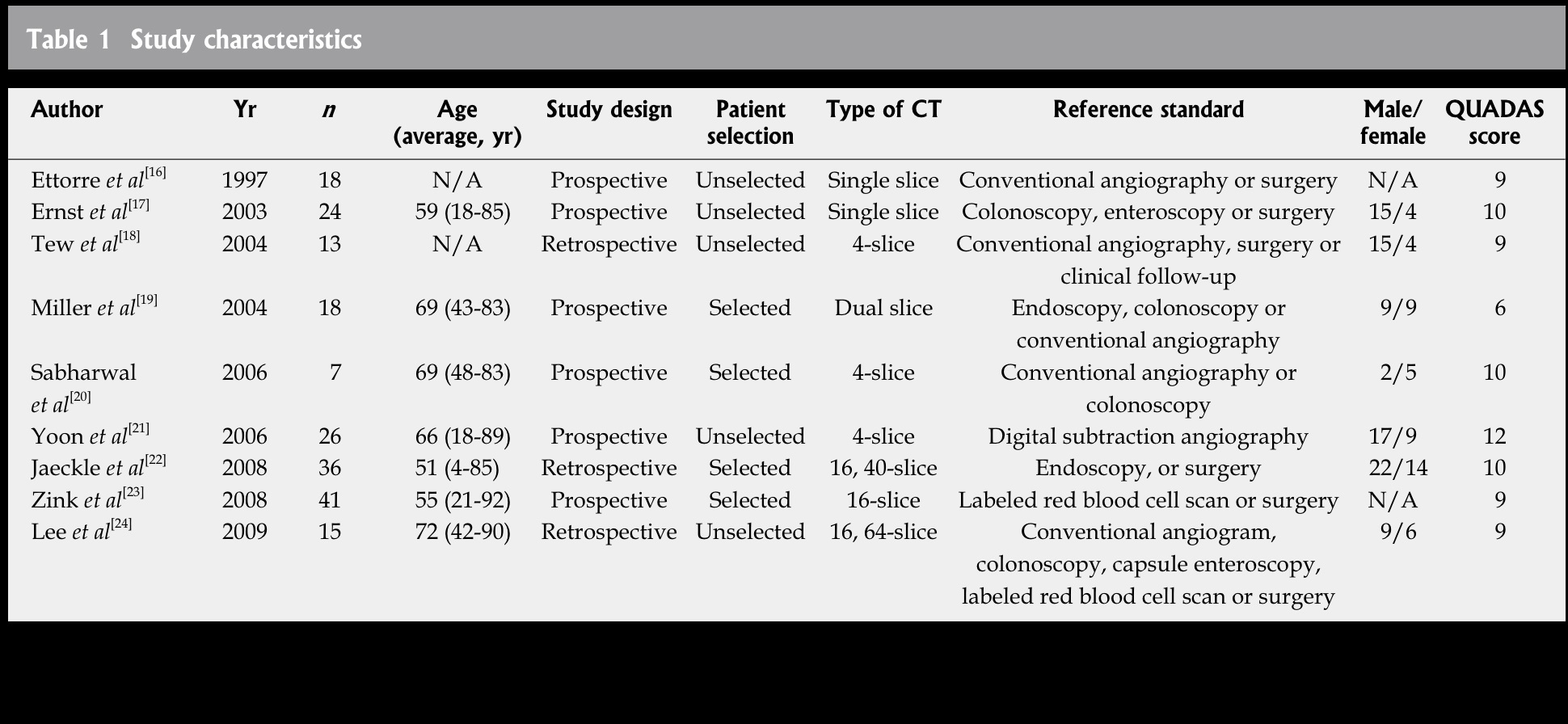
这一建议实际上改变急性消化道出血的临床诊断路径。 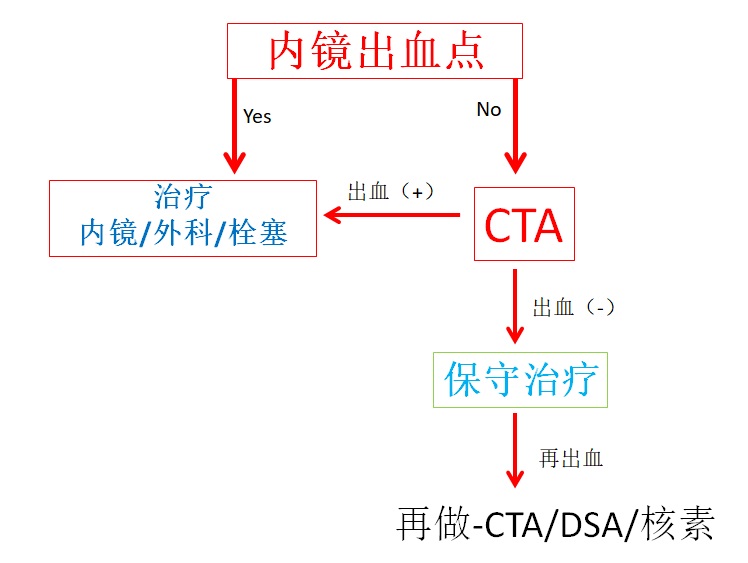 Outcome of negative CTA in acute GIH
°28/46 lower GIH (60%)
CTA 为阴性的病例,保守治疗的%高。 High % of conservative treatment after neg CTA
CTA阴性的急性下消化道出血,介入的男女们,似乎可以懒床,或打高尔夫或购物
IR man or woman,,it seems you can stay in bed, or go on golfing, or shopping
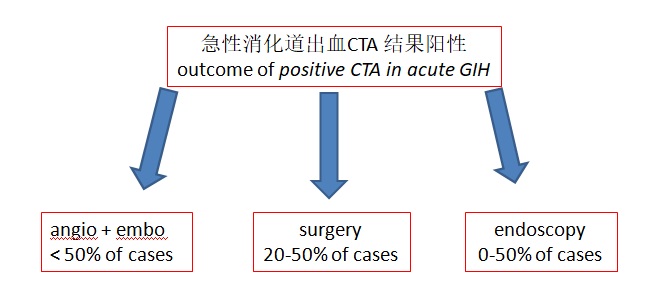
急性胃肠道出血CTA 阳性的结果(Outcome of positive CTA in acute GIH),我们能够根据急性消化道出血CTA阳性的结果决定是否患者需要外科,或再次内镜治疗,或血管造影,或者仍然等待 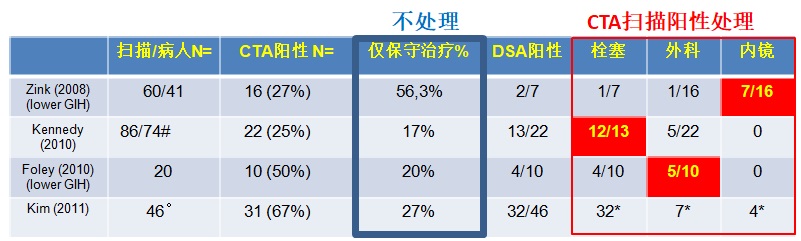
* not specified whether in post/neg CTA
# 59/74 lower GIH (80%)
°28/46 lower GIH (60%)
 甚至在CTA阳性的情况下,也并没有一个准确的指南可提供,但介入男女们应该开始时刻准备啦!
there is no clear algorithm, even in positive CTA cases, but be ready to intervene, IR man or woman
 核素扫描与CTA,我们应该联合它们吗?
Zink et al “Disagreement between Tc-99m RBC and CTA for acute lowerGIH” 2008, AJR
* angio + in 2/10;embo in 1; surgery in 2; conservative 8/11
尽管CTA和核素扫描比较不一致,但如果仅仅核素扫描阳性,很多病人似乎保守治疗更合适....,所以
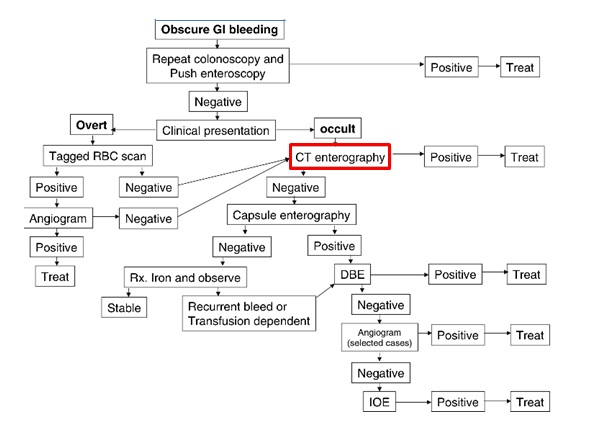
在日常工作中,急性消化道出血,CTA是否应该成为常规?一种观点认为,做CTA我们不会是在浪费时间吗? 似乎并不如此,很多CTA是阴性的,有时间决定栓塞/外科/内镜。当CTA时阴性,并不需要积极地进行有创的治疗,可以等着瞧(wait and see...)。我们只需套单行造影剂导致的肾损伤,和电离辐射的影响。尽管发生率低,而且影响是轻微的。 急性消化道出血的方法学 Kim et al, J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2011
我们需要全部都增强吗?Do we need all enhanced series? 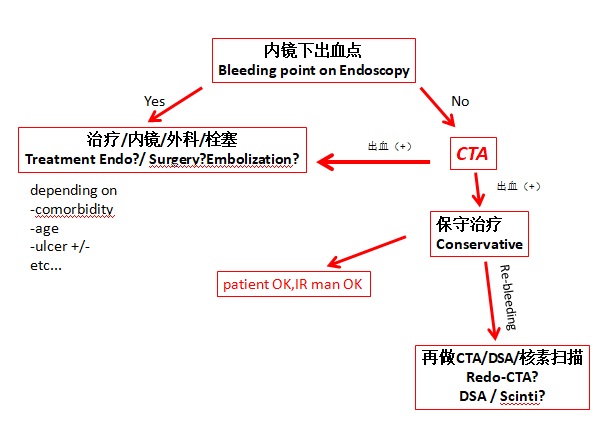 P Goffette CIRSE 2009 慢性和不明原因(隐匿性)消化道出血和CTA(do you see CTA?)
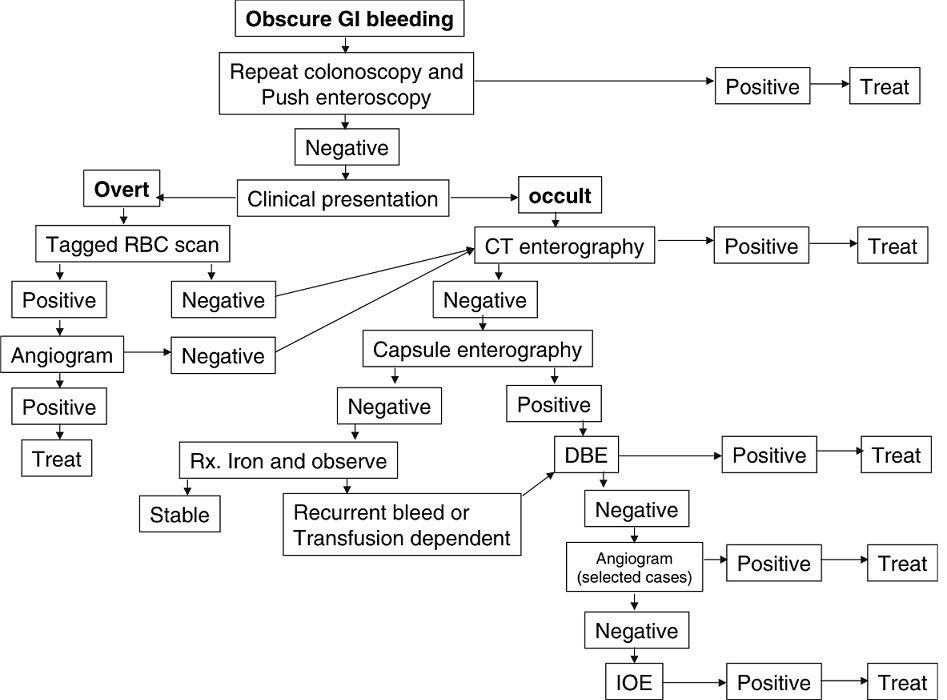
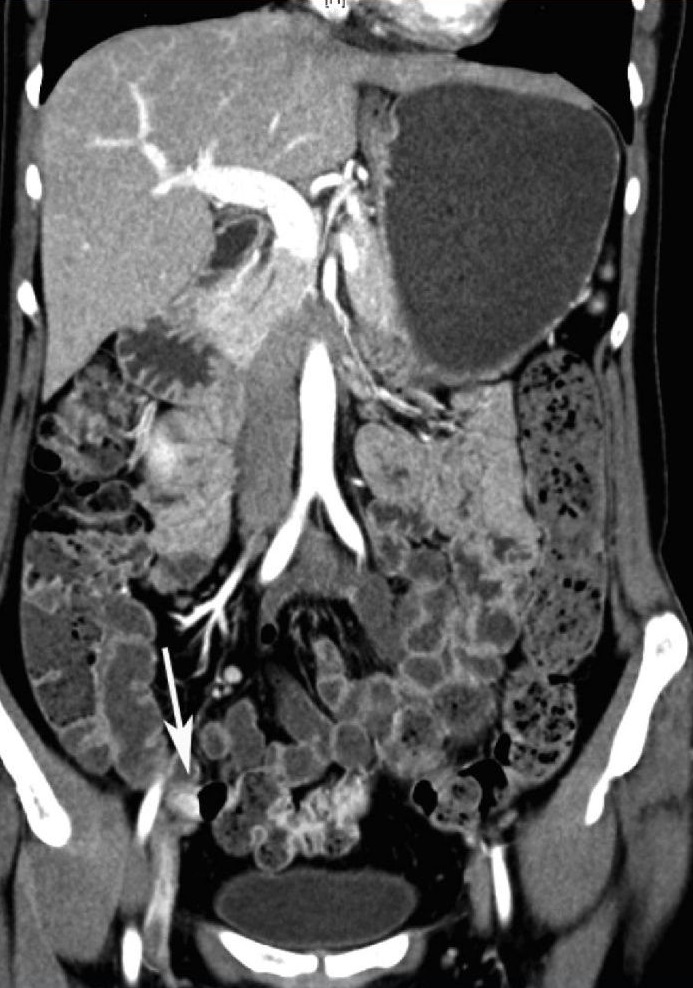
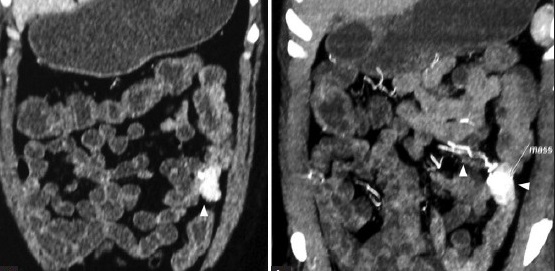
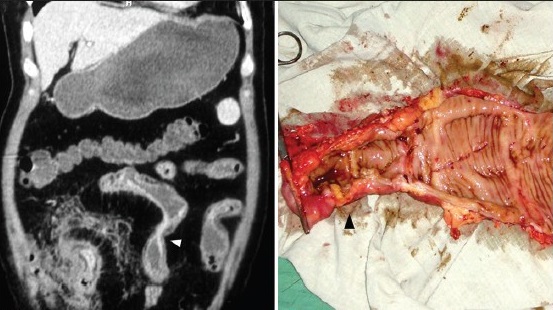
在慢性或隐匿性消化道出血的诊断路径中,甚至看不出CTA的作用 CTA and chronic/occult/obscure GIH
CTA and chronic/occult GIH(Huprich et al, Radiology, Sept 2011)
CTE扫描技术和CTA技术相似,64-128排,三期CTA;64 x 0.6mm overlapping projections和MPR重建。
不明原因的消化道出血为什么不能联合CTA的动脉造影?Obscure GIH: why not combining arteriography with CTA?
CTA-Mesentericography for obscure GIH
retrospective: 2002-2006 N=6
prospective: 2006-2009 N=7
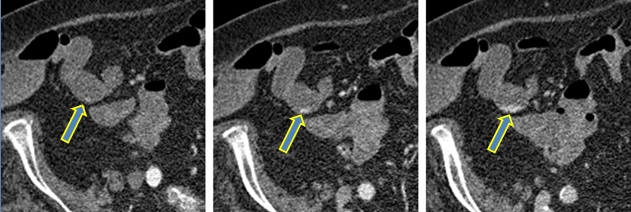
1. 主动脉-十二指肠瘘 YES“we feel that MDCTM cannot be recommended in general...” 胃肠道出血是否每个人都需要CTA? GI-hemorrhage; Should all patients be imaged with CTA? CTA technique of first choice, sens>90%, spec.>80%
Signs: contrast extravastion in duodenum, peri-graft fluid,
peri-graft soft tissue mass, peri-graft air, focal bowel wall
thickening, absence fatplane vessel wall - bowel wall
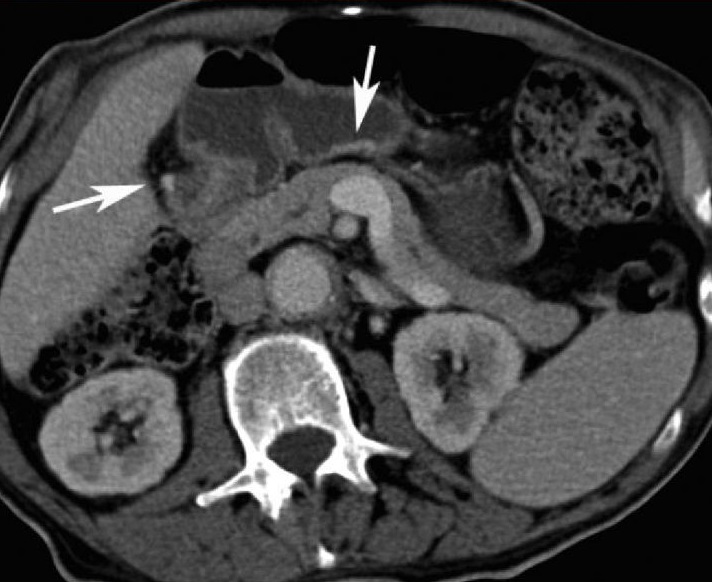
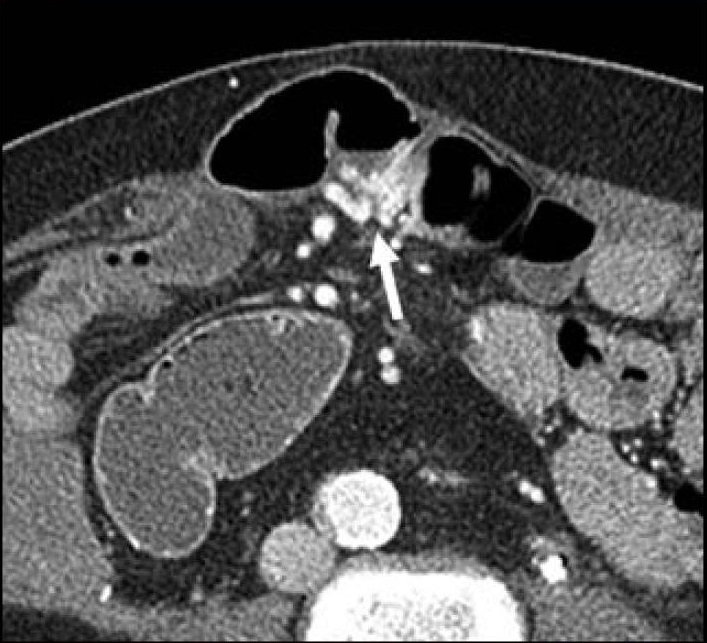
2. 胆道出血/胰腺出血 Hemobilia / hemosuccus pancreaticus
CTA technique of first choice
Endoscopy limited value for diagnosis and treatment
Embolization treatment of choice
CTA for treatment planning
Hyare et al. MDCT CT angiography compared with DSA in diagnosing major arterial hemorrhage in inflammatory pancreatic disease. Eur J Radiol. 2006: 59, 295-300
3. 其它原因 Maybe(可能需要进行CTA)
Endoscopy more often diagnostic in upper than lower GI tract*
Risk factors for CIN present?
Radiation risk (young patient)?
*Most common causes: upper GI bleed = ulcer bleed ; lower GI bleed = diverticular bleed
文献中CTA诊断消化道出血的结果 1. 动物实验
Animal study GI hemorrhage in pigs
CT detection of hemorrhage > 0.3 ml./min.
(Angio detection GI hemorrhage > 0.5 ml./min.)
Kuhle et al. Detection of active colonic hemorrhage with use of helical CT: findings in a swine model.Radiology 2003; 228: 743-52.
2. Literature results CTA -review
Pooled sens. 86% (95% CI 78–92%)
Pooled spec. 95% (95% CI 76–100%)
Chua et al. Diagnostic accuracy of CTA in acute GI bleeding. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. . 2008; 52: 333-8
4. 回顾性研究3. DSA作为参考标准,50例病人
Pooled sens. 88%
Retrospective study, 86 CTA’s in 76 pts.with acute GIH
Sens. 79%, spec. 95%, accuracy 91%
PPV(阳性预测值) 86%, NPV(阴性预测值) 92%
Kennedy et al Active GIH with CTA: a 41/2-year retrospective review. . JVIR 2010; 21: 848-55
Retrospective study in 26 pts. with confirmed acute GIH
Sens. 92% (24/26)
Jaeckle et al Detection and localization of acute upper and lower GI bleeding with arteria lphase MDCT. . Eur Radiol. 2008; 18: 1406-13
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||